How — and why — to fit more fiber and fermented food into your meals

UTI in older women: Why postmenopausal women are susceptible to urinary tract infection, and what to do about it

Can a routine vaccine prevent dementia?

Some adults may need a measles booster shot. Who should get one and why?

Less butter, more plant oils, longer life?

Healthier planet, healthier people

Counting steps is good — is combining steps and heart rate better?

Appendix pain: Could it be appendicitis?

Can saw palmetto treat an enlarged prostate?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond
Mind & Mood Archive
Articles
Putting off retirement may benefit your brain, health, and longevity
The purpose and engagement of a job you love can keep you healthy and connected.
Image: © monkeybusinessimages/Thinkstock
While many women dream of kicking back and relaxing into retirement, there's increasing evidence that in some cases, it's better for your brain and your health to keep your nose to the grindstone a little longer.
"The research to date is mixed, but it tends toward the positive — that is, for many people, there are health benefits to working longer," says Dr. Nicole Maestas, associate professor of health care policy at Harvard Medical School.
Alzheimer’s wake-up call
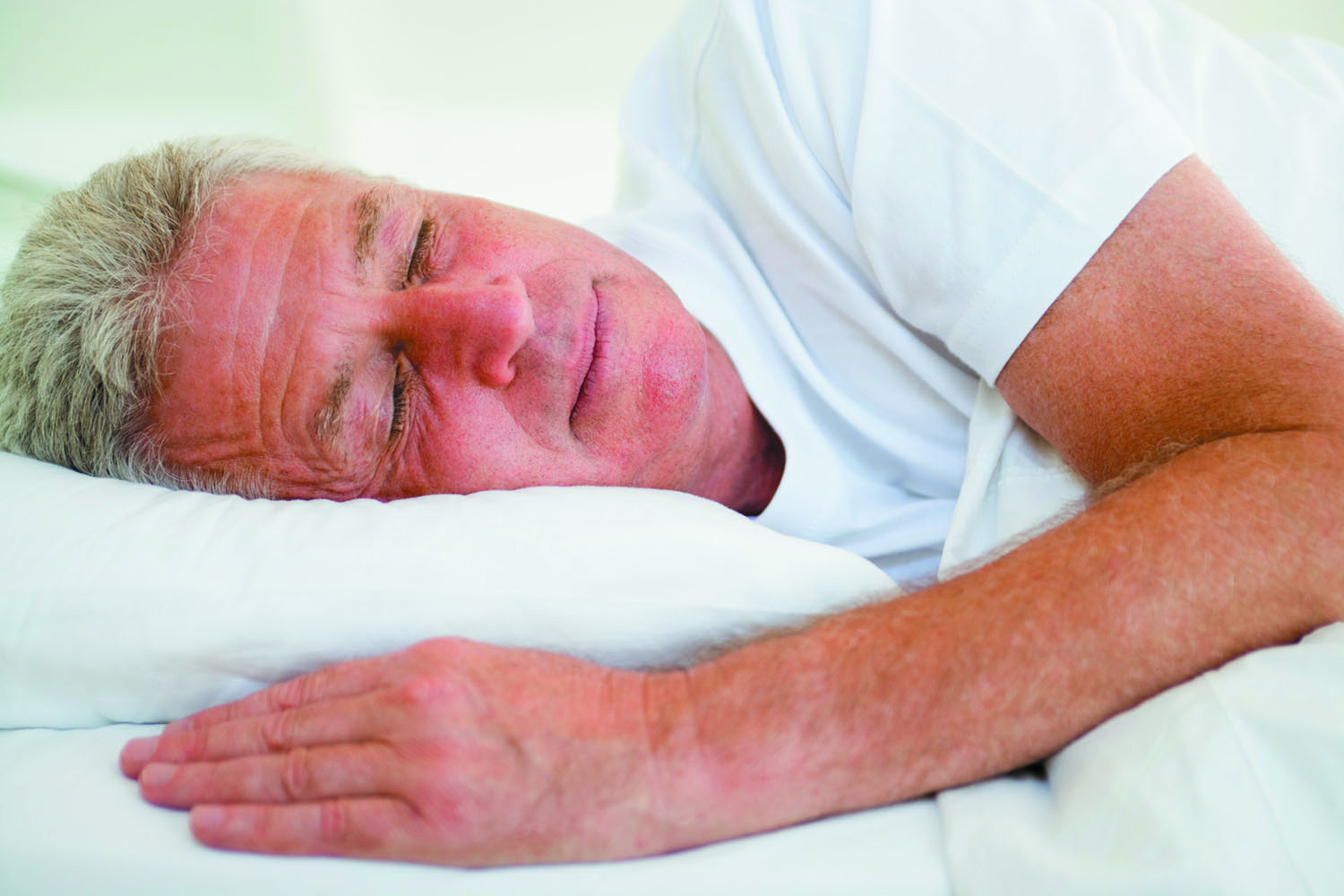
Can getting quality sleep help prevent the disease?
Image: © Monkey Business Images/Thinkstock
A good night's sleep does more than rejuvenate you for the next day. It may help protect you against Alzheimer's disease. Research has begun to show an association between poor sleep and a higher risk of accumulating beta-amyloid protein plaque in the brain, one of the hallmarks of the disease.
"Observational studies have found that adults over age 65 with amyloid plaques in their brain have reduced slow-wave sleep, which is thought to play an important role in memory function, even though these people do not yet show signs of Alzheimer's, like memory loss and cognitive decline," says Dr. Brad Dickerson, associate professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School. "It may be that quality sleep could play a role in who may get Alzheimer's."
Better habits, better brain health
Exercising, maintaining good health, socializing, and learning new information may help keep you sharper, longer.
Everyone wants to live an active, vibrant life for as long as possible. And that goal depends on robust brain health. While we don't have a guaranteed way to prevent dementia, we do have increasing evidence that engaging in healthy lifestyle habits may help.
For example, a 2015 randomized controlled trial from Finland suggested that older adults with a number of healthy habits — such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and socializing — improved or maintained thinking skills and reduced the risk of cognitive decline.
How memory and thinking ability change with age
Scientists used to think that brain connections developed at a rapid pace in the first few years of life, until you reached your mental peak in your early 20s. Your cognitive abilities would level off at around middle age, and then start to gradually decline. We now know this is not true. Instead, scientists now see the brain as continuously changing and developing across the entire life span. There is no period in life when the brain and its functions just hold steady. Some cognitive functions become weaker with age, while others actually improve.
Some brain areas, including the hippocampus, shrink in size. The myelin sheath that surrounds and protects nerve fibers wears down, which can slow the speed of communication between neurons. Some of the receptors on the surface of neurons that enable them to communicate with one another may not function as well as they once did. These changes can affect your ability to encode new information into your memory and retrieve information that's already in storage.
8 non-invasive pain relief techniques that really work
| Image: Bigstock |
Sometimes pain has a purpose — it can alert us that we've sprained an ankle, for example. But for many people, pain can linger for weeks or even months, causing needless suffering and interfering with quality of life.
If your pain has overstayed its welcome, you should know that you have more treatment options today than ever before. Here, we've listed eight techniques to control and reduce your pain that don't require an invasive procedure — or even taking a pill.
This is your brain on alcohol
It's no secret that alcohol affects our brains. Although excessive drinking is linked to an increased risk of dementia, decades of observational studies have indicated that moderate drinking has few ill effects. However, a recent British study seems to have bad news for moderate drinkers.
Treating anxiety without medication
| Image: iStock |
If you suffer from anxiety, the constant, nagging feelings of worry can be troubling and hard to control. These feelings are usually intense and out of proportion to the actual troubles and dangers in your everyday life. They can make it hard to function at home, at work, or in social situations.
Anxiety can be treated with medication, but several mind-body approaches may also be effective.
Can relationships boost longevity and well-being?
Harvard research suggests meaningful relationships are a prescription for better emotional, mental, and physical health.
Image: © digitalskillet/Thinkstock
You probably know there are many ways to improve your well-being and chances of living longer, such as exercising more or eating better. But did you know that maintaining meaningful relationships also may play an important role in health, happiness, and longevity? "Good, close relationships appear to buffer us from the problems of getting old," says Dr. Robert Waldinger, a psychiatrist with Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
Eight decades of research
Dr. Waldinger is the current director of the Harvard Study of Adult Development, an ongoing analysis that's followed more than 700 men since they were teenagers in 1938. More than 60 of the original participants, now in their 90s, are still taking part.
Looking for early signs of Alzheimer’s
By the time memory loss shows up, the disease is well under way. Researchers are finding ways that may reveal brain changes sooner.
For a long time, memory loss was seen as the telltale sign of Alzheimer's disease. While this is certainly the most common symptom, it may not be the best way to identify the disease in its early stages.
"A major problem of Alzheimer's diagnosis, and ultimately effective treatment, is that by the time the first clinical symptoms appear, irreversible damage to the brain has already occurred," says Dr. Seth Gale, a neurologist with Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. "It is now believed that Alzheimer's-related changes begin in the brain at least a decade before any symptoms emerge."
7 questions to ask when you’re given a prescription for an opioid
A discussion with your doctor may minimize your chance of becoming dependent on or addicted to these powerful painkillers.
Opioid misuse is now one of most important health problems in the United States, rivaling smoking as a cause of death. Although news reports tend to focus on an opioid crisis among the young, the opioid epidemic is increasingly affecting older people as well. In fact, the rates of hospitalization for opioid overdoses among Medicare recipients quintupled from 1993 through 2012. Although older people are still less likely than younger ones to become addicted or succumb to opioid overdoses, they are more likely to suffer side effects from extended opioid use, including memory and cognition problems and falls.
"Opioid use and pain management is something we deal with constantly," says Dr. Michael L. Barnett, assistant professor of health policy at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. According to a report from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, nearly one-third of Medicare beneficiaries received at least one prescription for opioids in 2015, and those who did got an average of five such prescriptions or refills. Dr. Barnett and a team of his colleagues decided to investigate how Medicare recipients get opioid prescriptions in the first place.

How — and why — to fit more fiber and fermented food into your meals

UTI in older women: Why postmenopausal women are susceptible to urinary tract infection, and what to do about it

Can a routine vaccine prevent dementia?

Some adults may need a measles booster shot. Who should get one and why?

Less butter, more plant oils, longer life?

Healthier planet, healthier people

Counting steps is good — is combining steps and heart rate better?

Appendix pain: Could it be appendicitis?

Can saw palmetto treat an enlarged prostate?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up