How — and why — to fit more fiber and fermented food into your meals

UTI in older women: Why postmenopausal women are susceptible to urinary tract infection, and what to do about it

Can a routine vaccine prevent dementia?

Some adults may need a measles booster shot. Who should get one and why?

Less butter, more plant oils, longer life?

Healthier planet, healthier people

Counting steps is good — is combining steps and heart rate better?

Appendix pain: Could it be appendicitis?

Can saw palmetto treat an enlarged prostate?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond
Men's Health Archive
Articles
Sunscreen confusion
Men may not be doing all they need to protect themselves from sun damage and skin cancer.
Image: JupiterImages/Thinkstock
Proper protection against skin cancer continues to be relevant once a man hits age 65. "Unfortunately, ultraviolet [UV] exposure and damage is cumulative over our lifetimes," says Dr. Joseph Merola, a dermatologist with Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. "There is no safe age at which we can put down the sunscreen or stop thinking about sun protection."
Even if men are aware of the dangers of sun exposure, new research shows most do not follow basic guidelines. A study published June 17, 2015, in JAMA Dermatology found that only 14.3% of men surveyed reported they regularly use sunscreen. The study also found that men were more likely than women to never use sunscreen—43.8% of men compared with 27% of women—and perhaps most telling, only 7% knew what to look for on a sunscreen label.
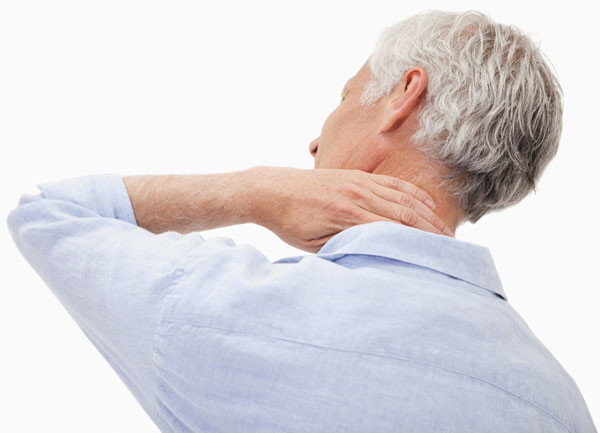
Turn away from neck pain
Poor lifestyle habits can trigger chronic neck pain that impedes daily activities and raises your risk of serious health issues.
Muscle strains caused by poor posture and sleeping positions often trigger neck pain.
Image: wavebreakmedia/Thinkstock
Neck pain is a nagging ailment that affects everyone at some time. In fact, approximately 80% of people experience neck pain during their lifetime, and 20% to 50% deal with it annually, according to Dr. Frank Pedlow, an orthopedic spine surgeon at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
Drink more water to cut calories, fat, and sugar?
Increasing daily water intake by one, two, or three cups daily can help reduce total calorie intake and lower a person’s intake of saturated fat, sugar, sodium, and cholesterol.
Risks of active surveillance for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancers
Men diagnosed with slow-growing prostate tumors that likely won’t be harmful during their lifetimes can often avoid immediate treatment. Instead, they can have their tumor monitored using a strategy called active surveillance. With this approach, doctors perform periodic checks for tumor progression and start treatment only if the cancer begins to metastasize, or spread. Active […]
The heart attack gender gap
Heart attacks strike men at younger ages than women. But survival rates are worse in women. Why?
Compared with men, women are less likely to recognize and act upon the symptoms of a heart attack.
Image: zaganDesign/Thinkstock
Imagine someone in the throes of a heart attack. If you picture a man clutching his chest in agony, that's understandable. At younger ages, men face a greater risk of heart disease than women. On average, a first heart attack—the most common manifestation of this prevalent disease—strikes men at age 65. For women, the average age of a first heart attack is 72.
Retired men at work
Retirement is your reward for a long work life, but research suggests that continuing to work in some way may offer a big payday for your health.
Image: Thinkstock
If you are retired, or counting the days, you may want to rethink leaving the workforce behind forever. Recent research has found that seniors who continue to work after age 65 are healthier than retirees.
"For many men, work defines who they are, and they still need to benefit from something meaningful and productive as they age, whether it's in their current job or field or something new," says Dr. William S. Pollack, assistant clinical professor in the Department of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School. "Work can boost confidence, self-esteem, and happiness, all of which can help men stay active and live longer."
Test may diagnose prostate cancer more accurately
A study in the December 2015 issue of The Lancet Oncology found that a new test, called STHLM3, is more helpful at detecting aggressive cancer than traditional tests for prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
The STHLM3 test is a blood test that analyzes a combination of six protein markers, more than 200 genetic markers, and various clinical data, such as age, family history, and previous prostate biopsies.

How — and why — to fit more fiber and fermented food into your meals

UTI in older women: Why postmenopausal women are susceptible to urinary tract infection, and what to do about it

Can a routine vaccine prevent dementia?

Some adults may need a measles booster shot. Who should get one and why?

Less butter, more plant oils, longer life?

Healthier planet, healthier people

Counting steps is good — is combining steps and heart rate better?

Appendix pain: Could it be appendicitis?

Can saw palmetto treat an enlarged prostate?

How does Ozempic work? Understanding GLP-1s for diabetes, weight loss, and beyond
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up